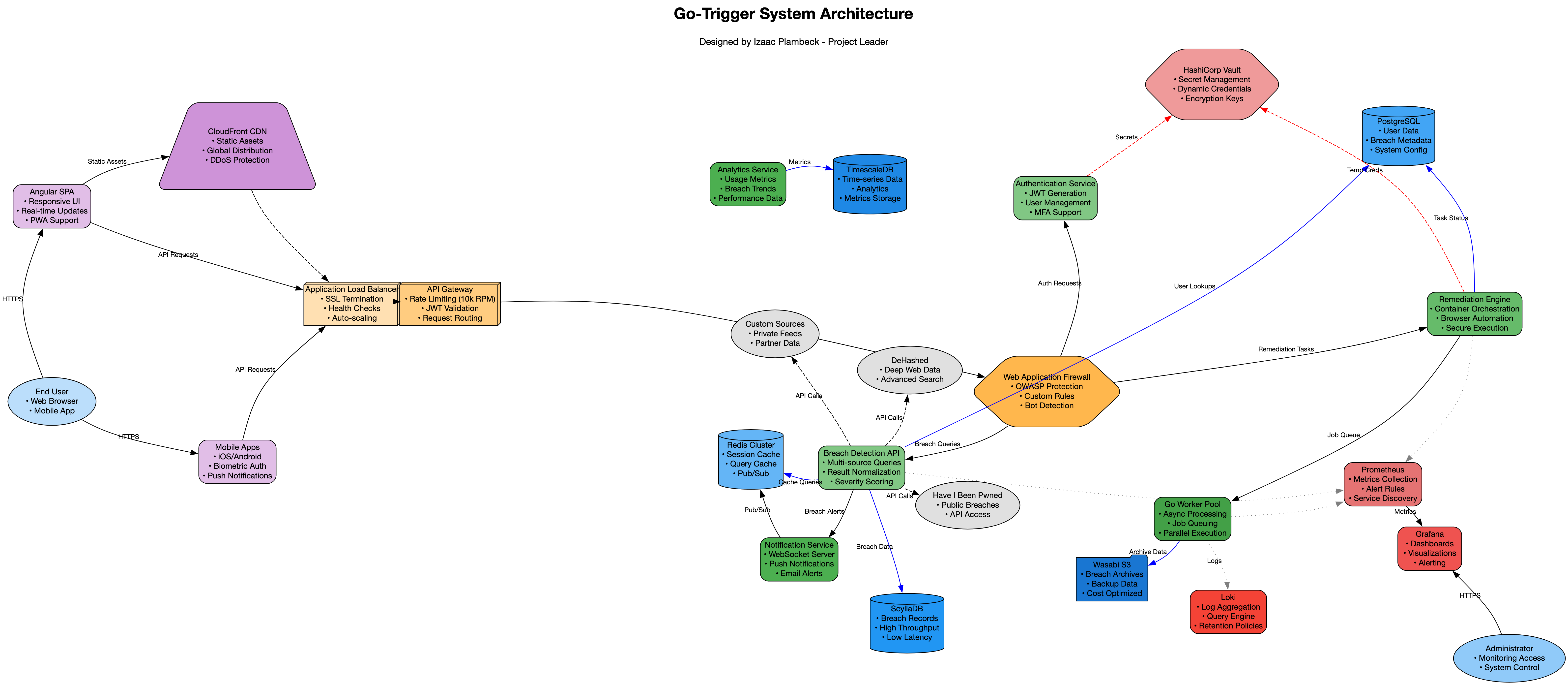
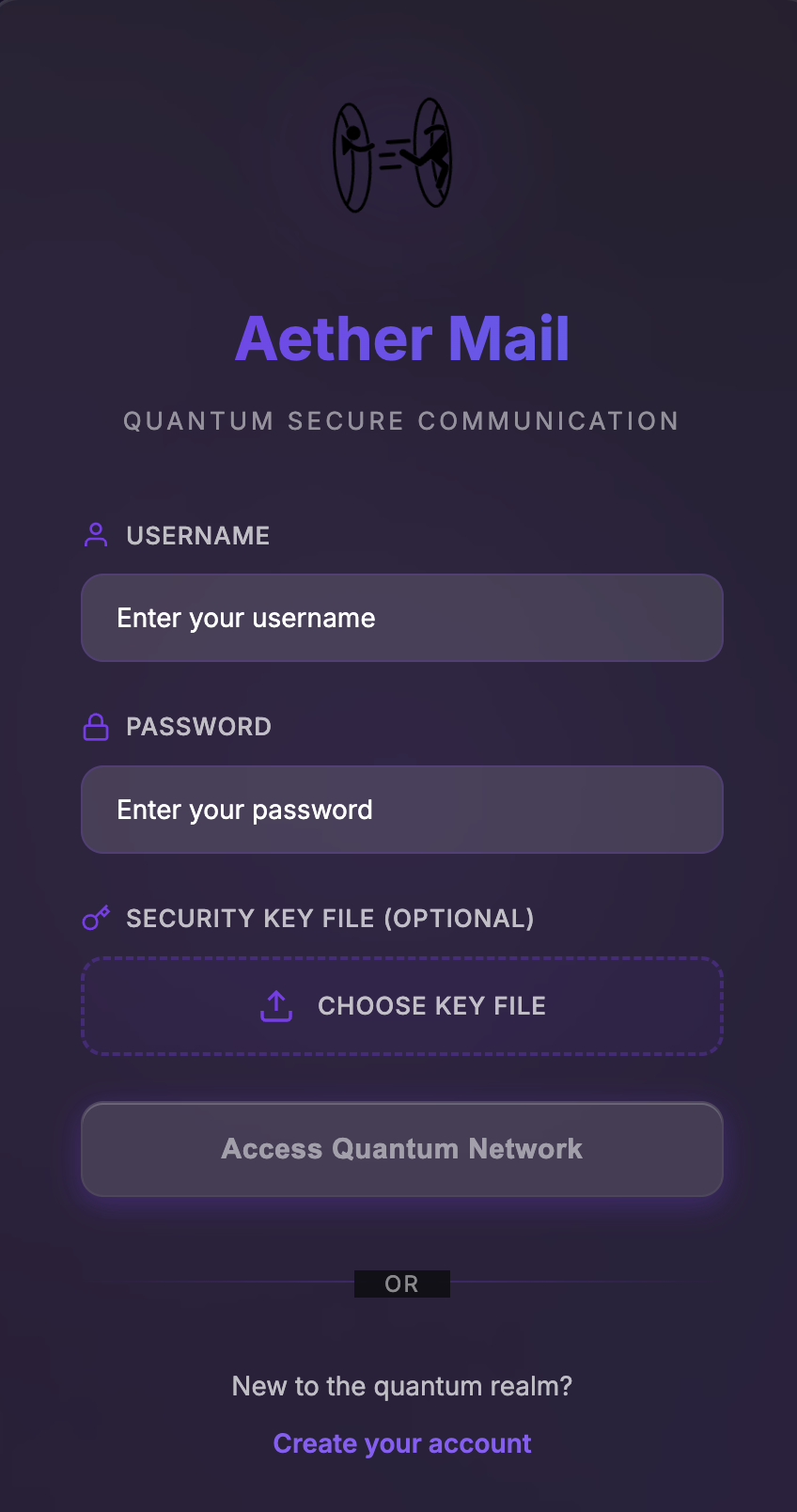
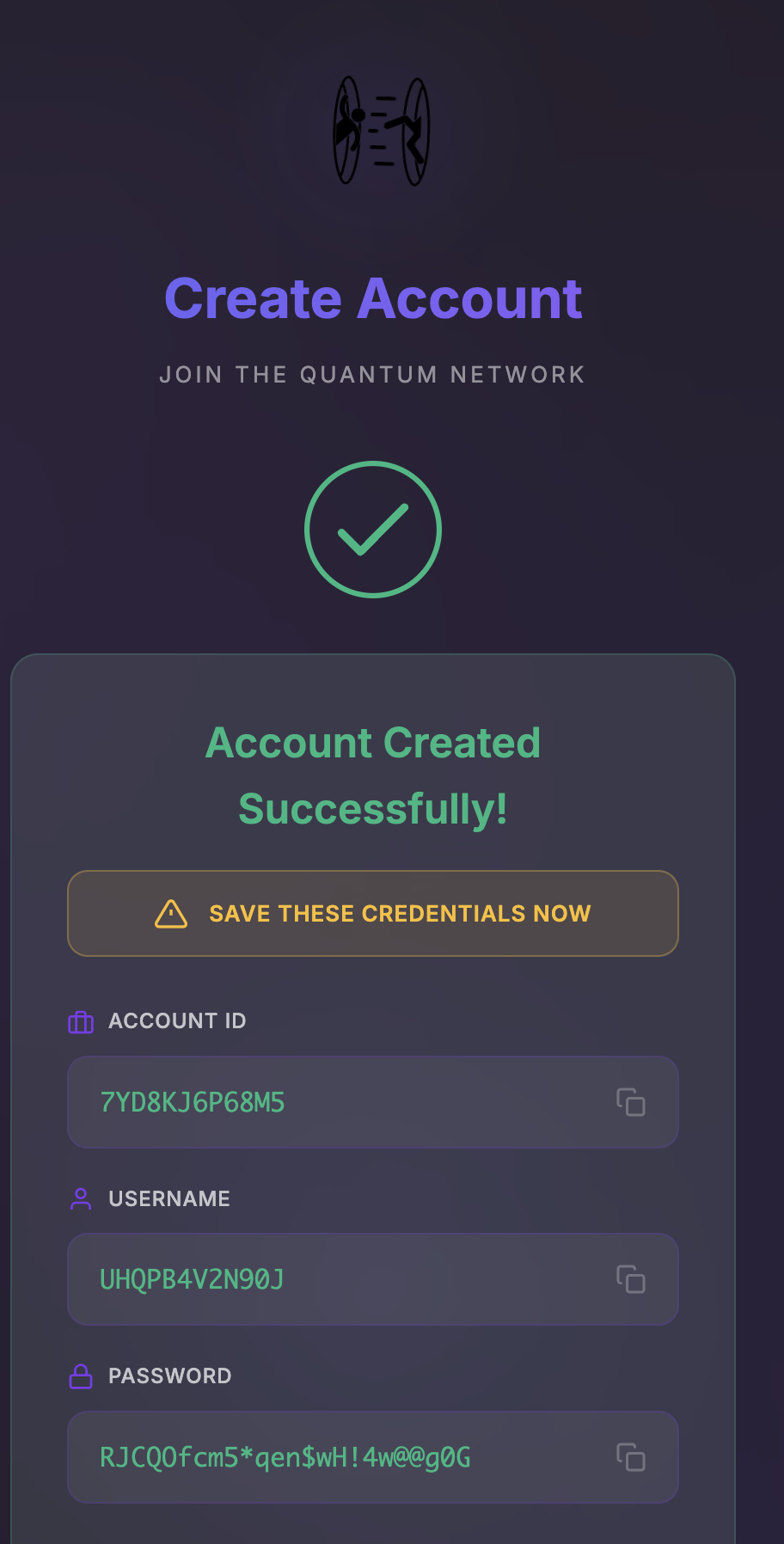
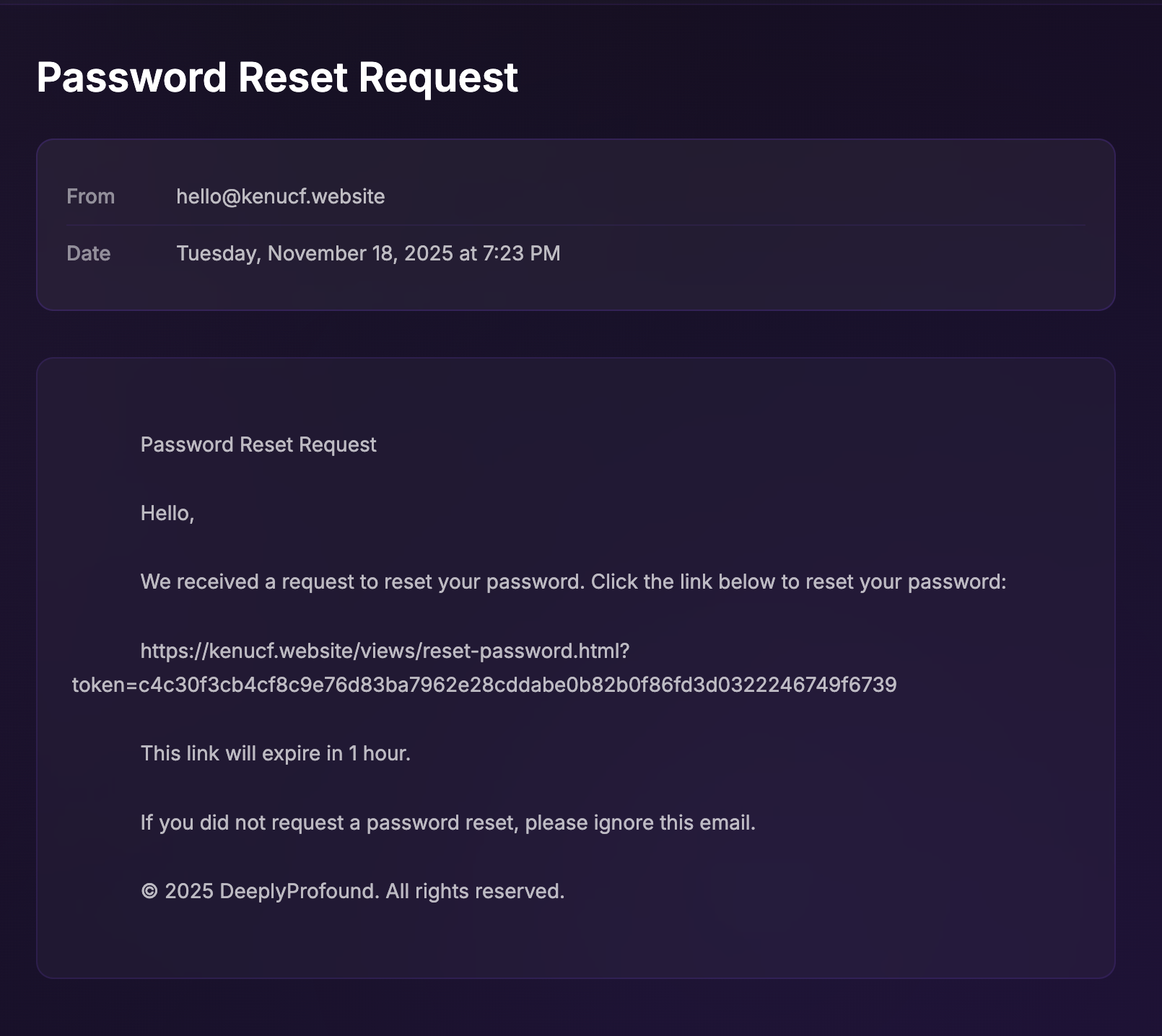
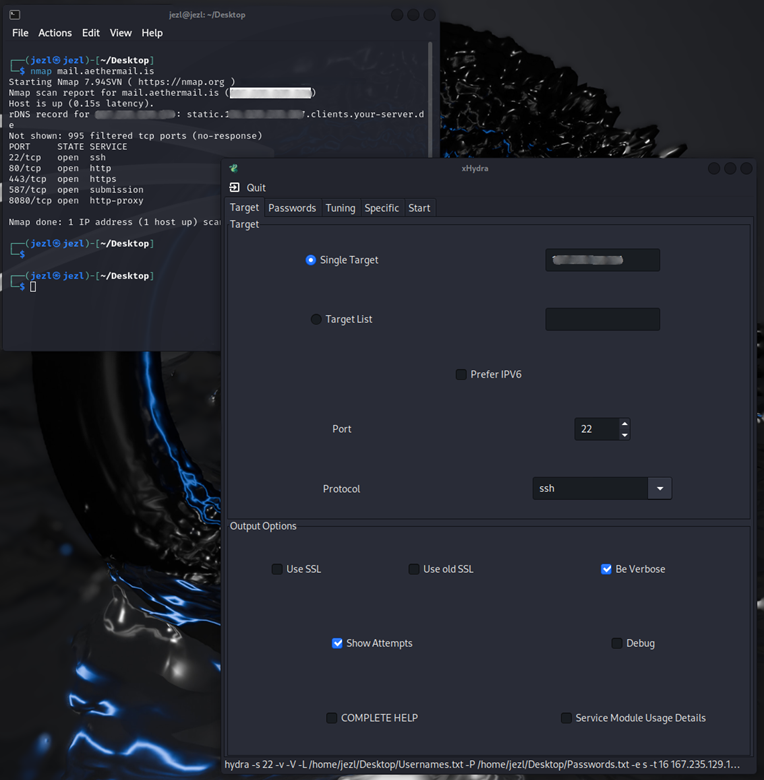
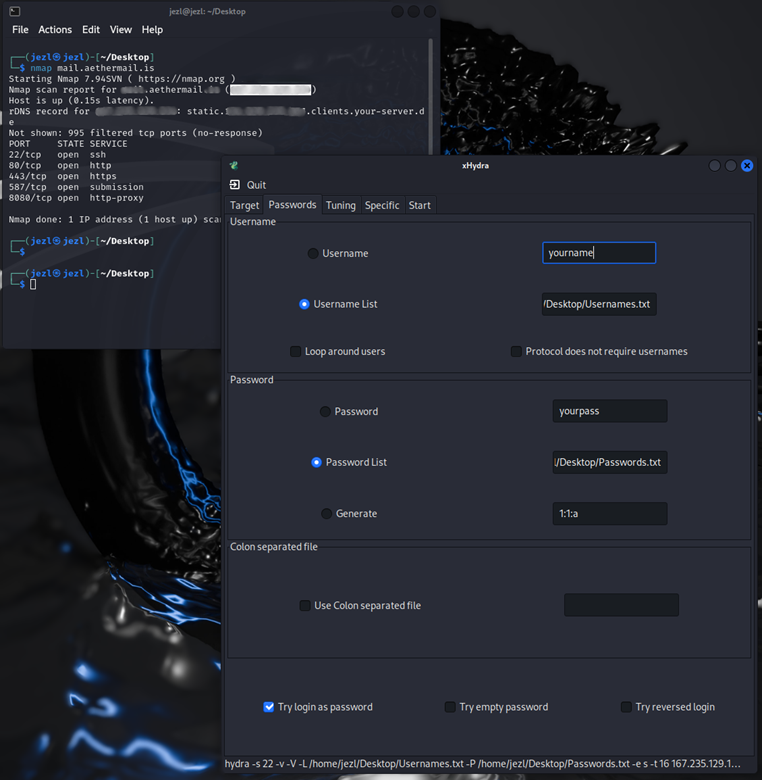
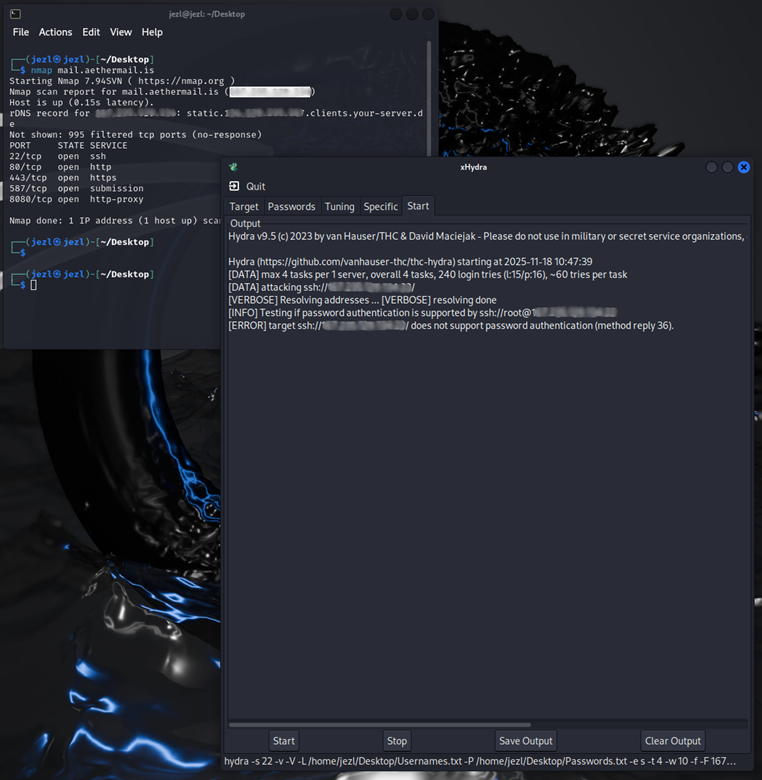
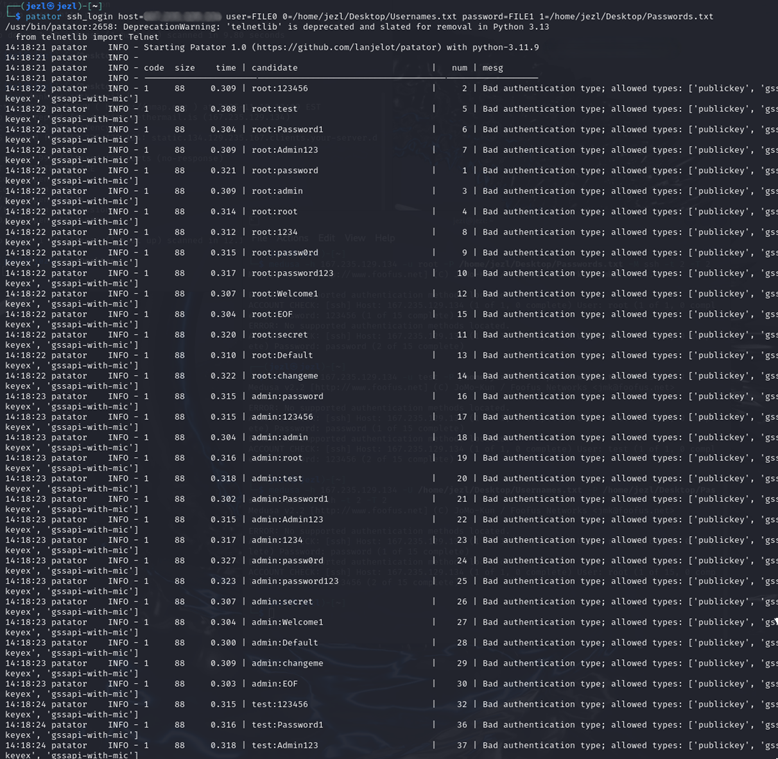
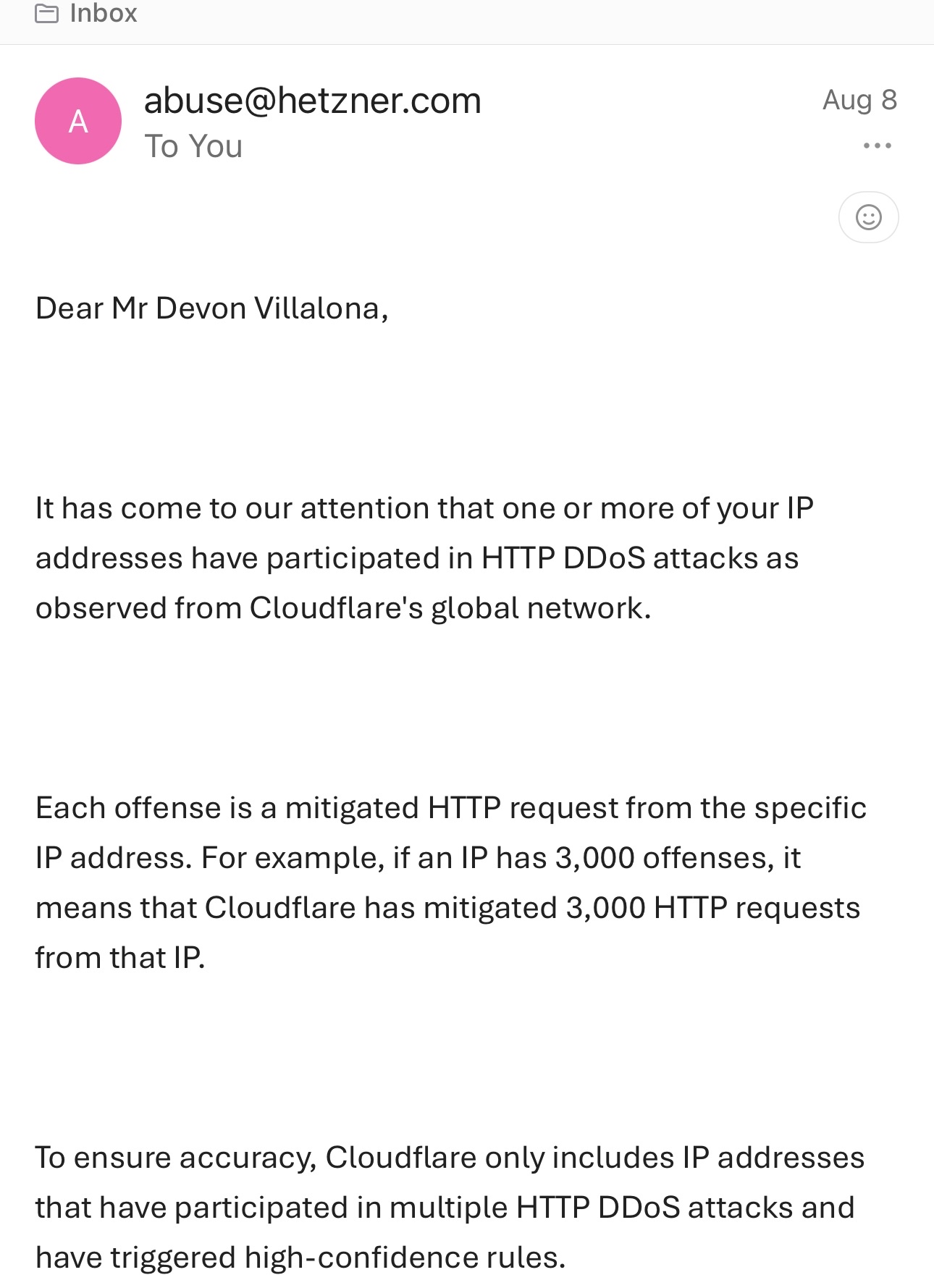
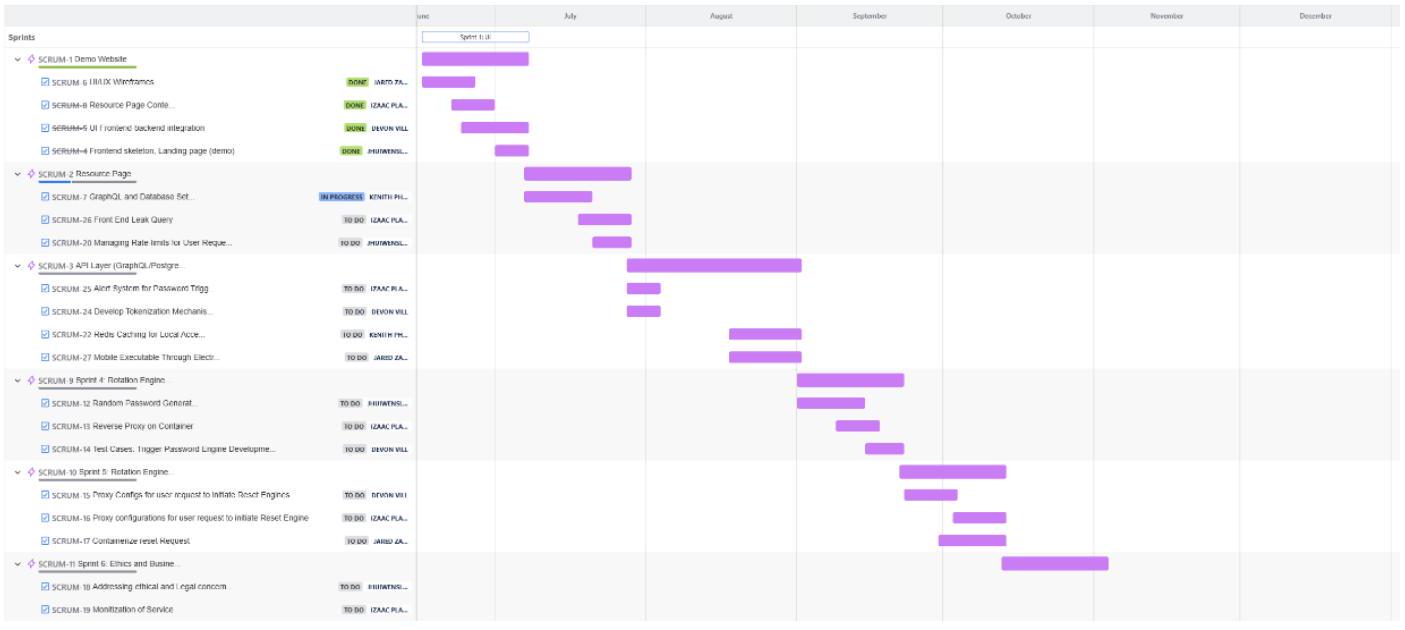
The Problem
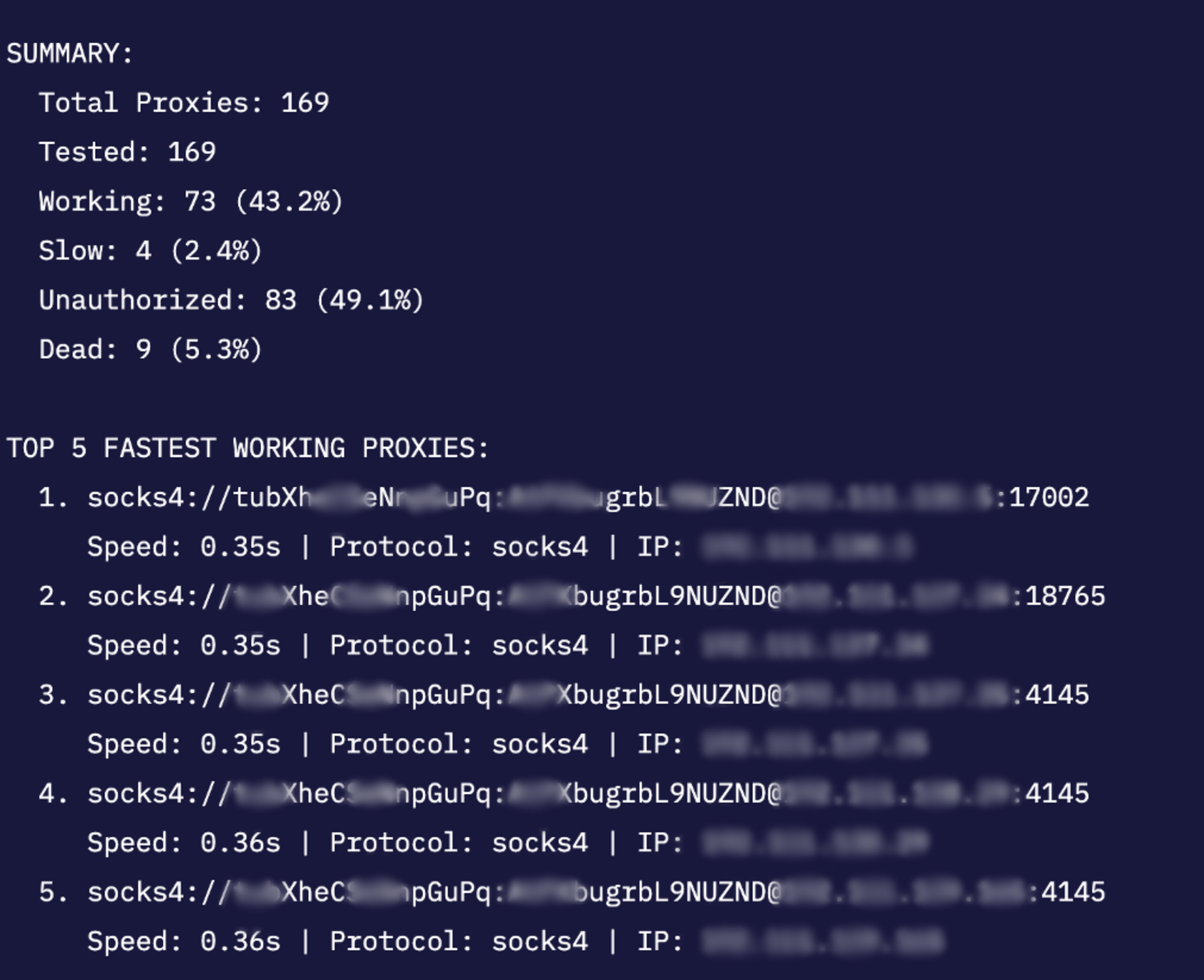
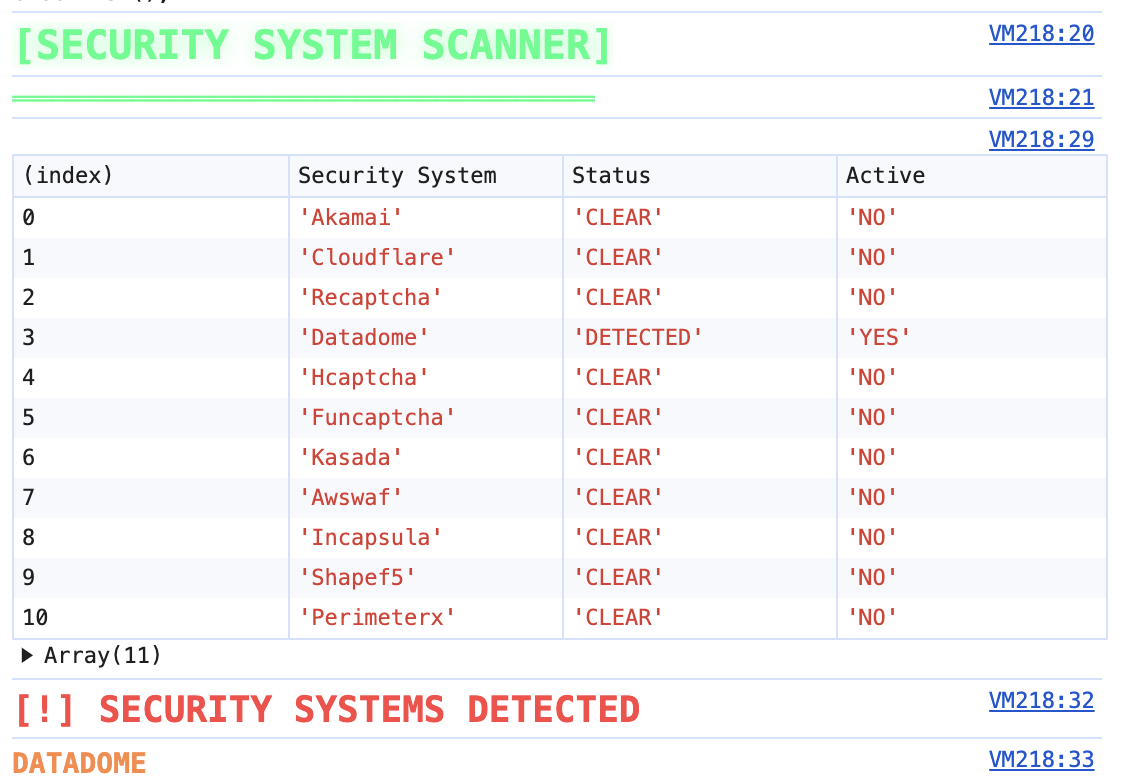
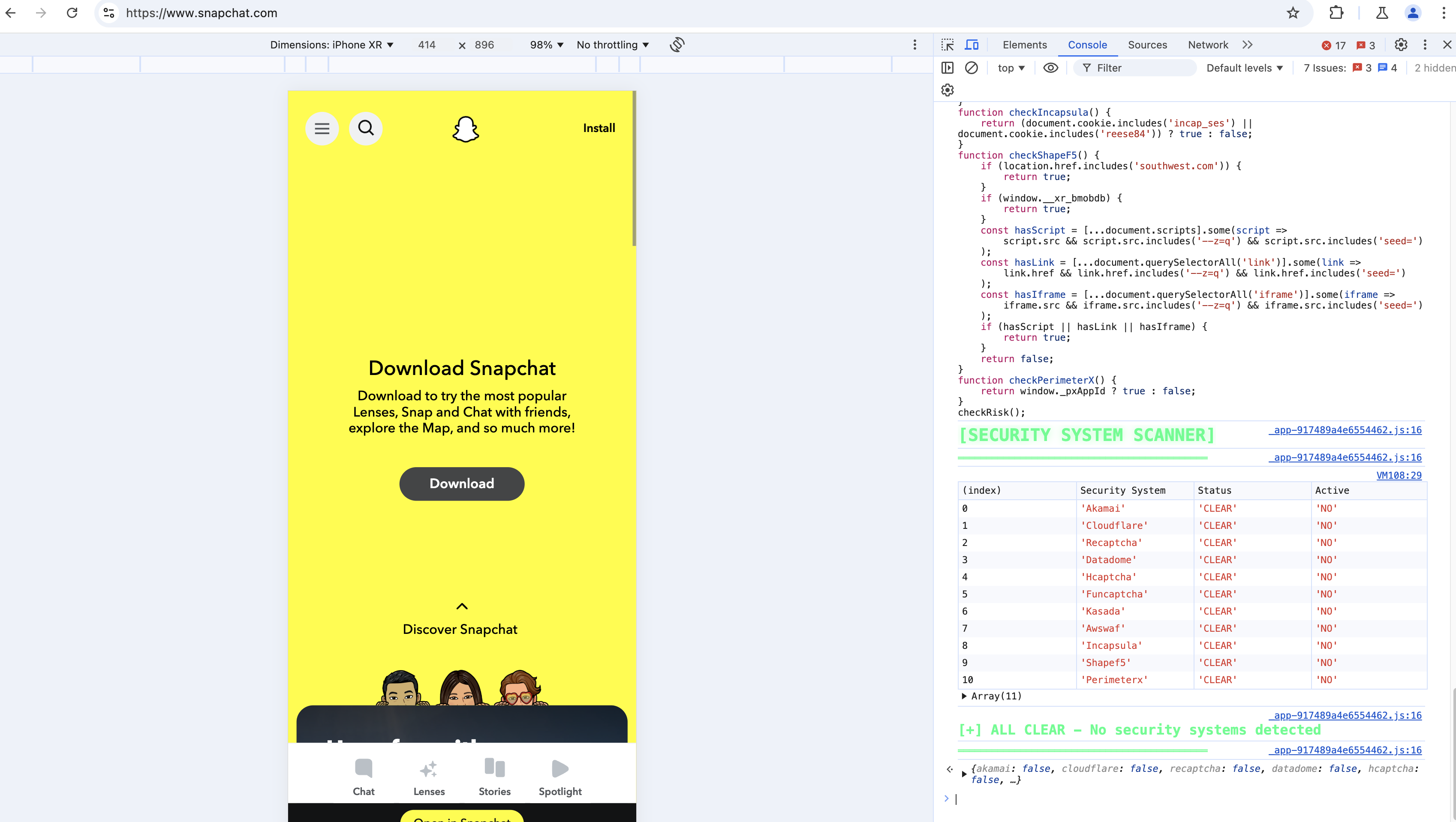
Our legitimate password rotation requests were flagged as HTTP DDoS attacks by Cloudflare's network, resulting in an abuse complaint from Hetzner.
Our Solution
- Implemented request rate limiting and exponential backoff
- Added user-agent rotation and request fingerprinting
- Distributed requests across multiple IP addresses
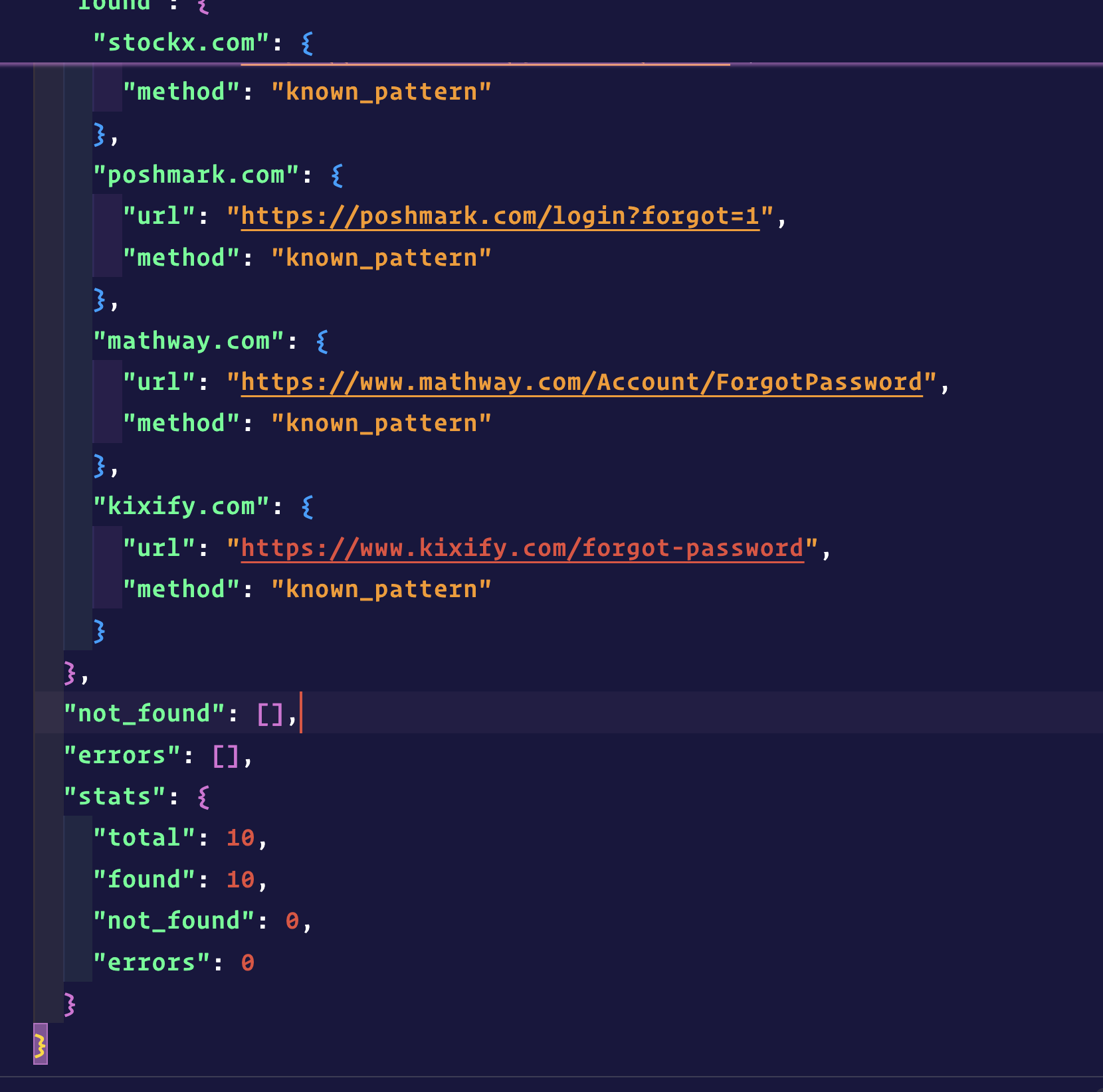
- Whitelisted our IPs with major CDN providers